No products in the cart.
Genomics
Karyotyping

Introduction
Karyotyping is a laboratory technique used to examine an individual’s chromosomes for genetic abnormalities or variations. It involves arranging and photographing chromosomes from a cell during metaphase of mitosis, when they are most condensed and visible under a microscope
Each species has a characteristic number of
chromosomes, and karyotyping helps identify any deviations from this normal number or any structural abnormalities within the chromosomes. It is particularly useful in diagnosing genetic disorders, assessing chromosomal sex (XX or XY), and understanding genetic relationships in research.
Karyotyping can be performed on various types of biological samples depending on the purpose of the analysis:
Karyotyping can be performed on various types of biological samples depending on the purpose of the analysis:
Blood: Peripheral blood is a common source of cells for karyotyping. White blood cells (lymphocytes) are often cultured to obtain metaphase cells for analysis. This method is routinely used in clinical settings for
diagnosing chromosomal abnormalities.
Amniotic Fluid: During prenatal diagnosis, amniotic fluid can be collected via amniocentesis (usually performed around the 15th-22th week of pregnancy). Cells from the amniotic fluid are cultured to obtain metaphase cells for karyotyping, which helps assess the fetal chromosomes for abnormalities.
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): This involves sampling of chorionic villi (tissue from the placenta) usually around the 15th-22th week of pregnancy. Cells from the chorionic villi can be cultured and karyotyped to evaluate the fetal chromosomes for genetic disorders. Bone Marrow: In cases where there is suspicion of a leukemia (blood cancer mutation) bone marrow cells may be analyzed by karyotyping to detect chromosomal abnormalities in the hematopoietic cells.
Product of conception: In some cases, solid tissues like skin, toe, finger and placenta samples (with patient consent due to ethical issues) can be used for karyotyping, especially when investigating genetic mosaicism or chromosomal abnormalities.
Amniotic Fluid: During prenatal diagnosis, amniotic fluid can be collected via amniocentesis (usually performed around the 15th-22th week of pregnancy). Cells from the amniotic fluid are cultured to obtain metaphase cells for karyotyping, which helps assess the fetal chromosomes for abnormalities.
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): This involves sampling of chorionic villi (tissue from the placenta) usually around the 15th-22th week of pregnancy. Cells from the chorionic villi can be cultured and karyotyped to evaluate the fetal chromosomes for genetic disorders. Bone Marrow: In cases where there is suspicion of a leukemia (blood cancer mutation) bone marrow cells may be analyzed by karyotyping to detect chromosomal abnormalities in the hematopoietic cells.
Product of conception: In some cases, solid tissues like skin, toe, finger and placenta samples (with patient consent due to ethical issues) can be used for karyotyping, especially when investigating genetic mosaicism or chromosomal abnormalities.
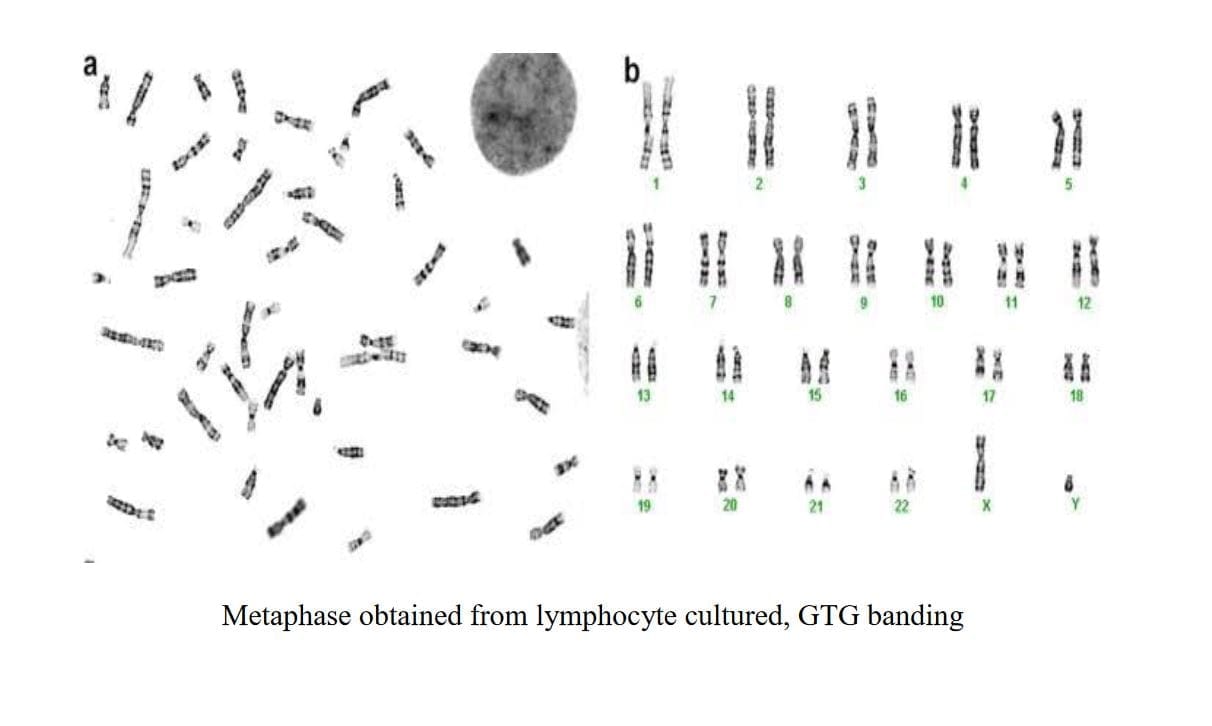
Peripheral Blood Lymphocyte Culture
Introduction
Peripheral blood lymphocyte culture involves isolating and culturing lymphocytes from a sample of peripheral blood. This technique allows to examine the chromosomes of lymphocytes to detect genetic abnormalities or to study their responses to different stimuli.
Principle
The principle behind peripheral blood lymphocyte culture is to provide an environment in which lymphocytes can divide and grow outside the body. By adding specific growth factors and nutrients to the culture medium, lymphocytes are stimulated to undergo cell division (mitosis). This process is crucial for preparing cells for analysis, such as karyotyping to analyze chromosome structure or genetic testing.
Methodology
Blood Collection: 1-2 ml sample of peripheral blood (usually venous
blood) is collected from the patient.
Isolation of Lymphocytes: Lymphocytes are separated from other blood components using techniques such as density gradient centrifugation.
Culturing Lymphocytes: The isolated lymphocytes are placed in a culture medium containing nutrients, growth factors (e.g., phytohemagglutinin), and other necessary components to stimulate cell growth.
Mitotic Stimulation: The culture is incubated to stimulate lymphocytes to undergo mitosis, during which chromosomes can be analyzed.
Harvesting Cells: After a suitable period of incubation (usually 72 hours), cells are harvested for analysis, such as karyotyping or genetic testing.
Isolation of Lymphocytes: Lymphocytes are separated from other blood components using techniques such as density gradient centrifugation.
Culturing Lymphocytes: The isolated lymphocytes are placed in a culture medium containing nutrients, growth factors (e.g., phytohemagglutinin), and other necessary components to stimulate cell growth.
Mitotic Stimulation: The culture is incubated to stimulate lymphocytes to undergo mitosis, during which chromosomes can be analyzed.
Harvesting Cells: After a suitable period of incubation (usually 72 hours), cells are harvested for analysis, such as karyotyping or genetic testing.

Amniotic Fluid(af) / Chorionic Villi(cvs) For Culture
Introduction
Amniotic fluid is the fluid that surrounds the
fetus in the amniotic sac during pregnancy. It contains fetal cells and other substances that can be used for various diagnostic tests, including karyotyping. Chorionic villi are tiny, finger-like projections of placental tissue that develop from the fertilized egg. They contain fetal cells and can be sampled for prenatal genetic testing, including karyotyping.
Principle
Karyotyping involves the visualization and analysis of the chromosomes of an organism. In the case of prenatal diagnosis using Amniotic fluid or Chorionic villus sample are cultured to increase their number.
These cells are then harvested and treated to prepare chromosome spreads. The spreads are stained and examined under a microscope to identify and analyze the number, size, and shape of chromosomes.
Methodology
1. Amniocentesis/ Chorionic Villus: A procedure where a small amount of amniotic fluid (10- 12ml) is withdrawn from the amniotic sac surrounding the fetus
/ chorionic villi is obtained either transcervically (through the cervix) or transabdominally (through the abdomen)
2. Cell Culture: Fetal cells present in the AF/CVS are cultured to increase their number.
3. Chromosome Preparation: Cells from the culture are harvested and treated to arrest them in metaphase (a stage of cell division where chromosomes are most visible).
4. Staining and Analysis: Chromosomes are stained using specific dye (giemsa), and then analyzed under a microscope to determine any abnormalities.
2. Cell Culture: Fetal cells present in the AF/CVS are cultured to increase their number.
3. Chromosome Preparation: Cells from the culture are harvested and treated to arrest them in metaphase (a stage of cell division where chromosomes are most visible).
4. Staining and Analysis: Chromosomes are stained using specific dye (giemsa), and then analyzed under a microscope to determine any abnormalities.
Bone Marrow Culture For Karyotyping
Introduction
Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found inside bones, responsible for producing blood cells. It contains stem cells that give rise to both red and white blood cells. Bone marrow can be sampled for diagnostic
purposes, including karyotyping, to assess chromosomal abnormalities.
Principle
Karyotyping involves the analysis of an individual’s chromosomes to detect any structural or numerical abnormalities. Bone marrow karyotyping specifically examines the chromosomes within the bone marrow
cells to diagnose conditions such as leukemia,(CML),(AML),(ALL) myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), and other hematologic disorders.
Methodology
Bone Marrow Aspiration: A procedure where a needle is inserted into a
bone (often the hip bone) to withdraw a small sample of bone marrow.
Cell Culture (Optional): In some cases, bone marrow cells may be cultured to increase their number before chromosome analysis.
Chromosome Preparation: Cells from the bone marrow sample are treated to arrest them in metaphase (a stage of cell division where chromosomes are visible).
Staining and Analysis: Chromosomes are stained with specific dyes and examined under a microscope to identify and analyze their number, size, and structure
Cell Culture (Optional): In some cases, bone marrow cells may be cultured to increase their number before chromosome analysis.
Chromosome Preparation: Cells from the bone marrow sample are treated to arrest them in metaphase (a stage of cell division where chromosomes are visible).
Staining and Analysis: Chromosomes are stained with specific dyes and examined under a microscope to identify and analyze their number, size, and structure

Product Of Cenception (poc) For Karyotyping
Introduction
Products of conception (POC) refer to tissues (embryonic or fetal) and placental material expelled from the uterus during miscarriage or termination of pregnancy. These tissues contain fetal cells and can be analyzed
to determine chromosomal abnormalities through karyotyping.
Principle
Karyotyping involves the examination of an
individual’s chromosomes to detect any abnormalities. Products of conception karyotyping specifically involves the analysis of chromosomes from fetal tissues to
diagnose genetic disorders that may have led to miscarriage or fetal demise.
Methodology
Collection of POC: Tissues
from products of conception are collected following miscarriage or termination of pregnancy (required patient consent due to ethical issues).
Cell Culture (Optional): Fetal cells from POC may be cultured to increase their number for chromosome analysis.
Chromosome Preparation: Cells from POC are treated to arrest them in metaphase (a stage of cell division where chromosomes are visible).
Staining and Analysis: Chromosomes are stained with specific dyes and examined under a microscope to identify and analyze their number, size, and structure
Cell Culture (Optional): Fetal cells from POC may be cultured to increase their number for chromosome analysis.
Chromosome Preparation: Cells from POC are treated to arrest them in metaphase (a stage of cell division where chromosomes are visible).
Staining and Analysis: Chromosomes are stained with specific dyes and examined under a microscope to identify and analyze their number, size, and structure
Applications
- Diagnosis of genetic abnormalities such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13).
- Investigate the genetic mutations, deletions, duplications, and rearrangements associated with various genetic disorders.
Provides valuable information to parents about the genetic health of their unborn child (AF/CVS). - Identifies chromosomal abnormalities associated with leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma, MDS, and other blood disorders (Bone Marrow).
Provides information to parents about the genetic health of the fetus and risk assessment for future pregnancies (AF/CVS/POC).
Advantages
- Enables the study of chromosome structure and abnormalities, which is crucial in genetic disorders.
- Used in clinical settings to diagnose genetic disorders.
- Can detect chromosomal abnormalities early in pregnancy (AF/CVS).
- Helps healthcare providers choose appropriate therapies based on genetic findings.
- Helps in understanding the genetic factors contributing to miscarriage (POC).
- Assists in making informed decisions about future pregnancies and prenatal care.
- Facilitates genetic counseling and screening for inherited conditions.
Disadvantages
- Requires skilled technicians and specialized equipment for chromosome analysis.
- The process of cell culture and chromosome analysis typically takes a few days or weeks to complete.
- Variability in cell cultures can affect reproducibility of results.
- Invasive Procedure carries a small risk of complications and painfull, including miscarriage (AF/CVS).
- Dependent on successful collection of POC during miscarriage or termination.


